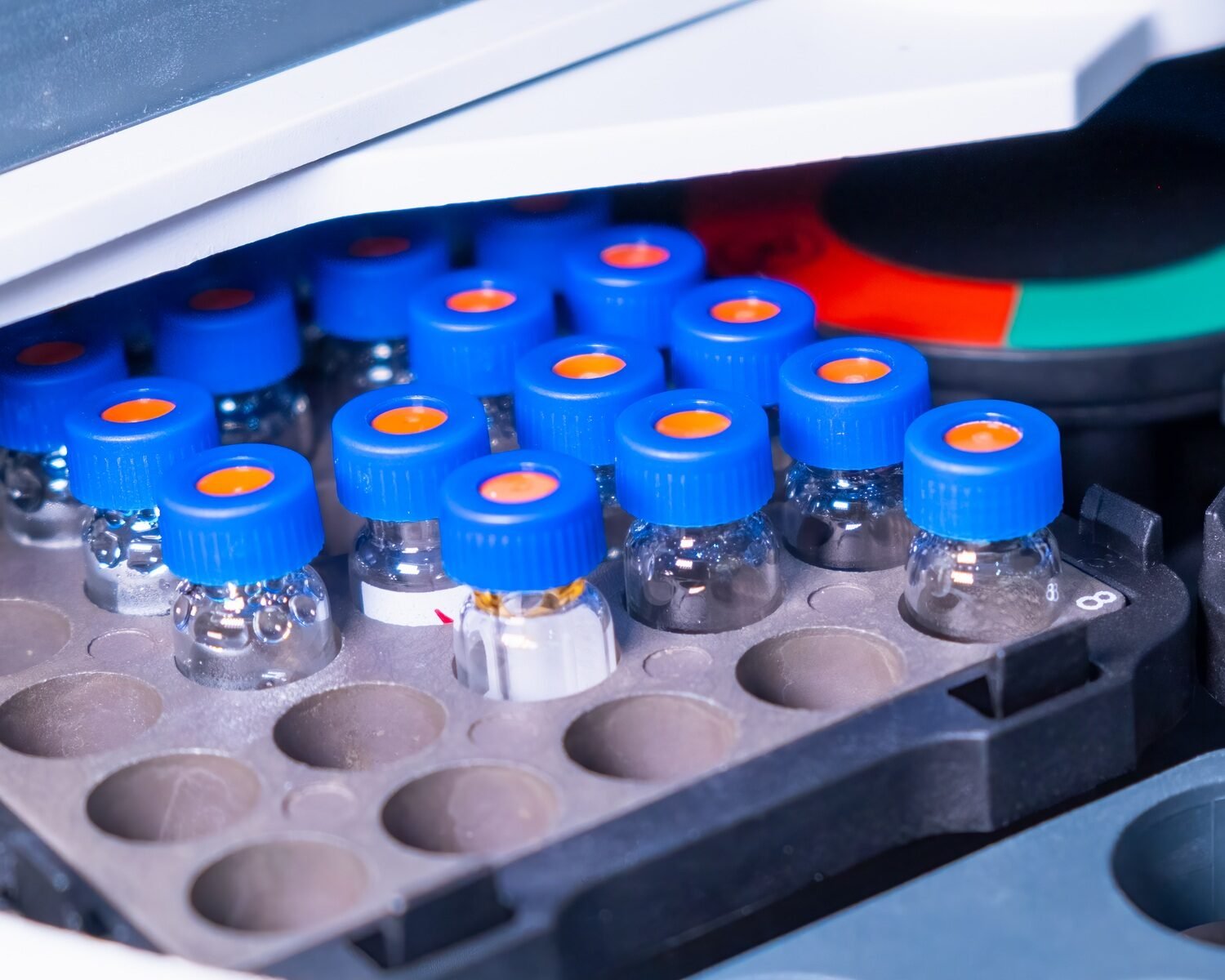
Introduction
When it comes to HPLC sample injection, choosing the right vial is about more than just volume—it’s also about diameter and neck size. These seemingly small factors can greatly impact injection accuracy, sample transfer, and system compatibility.
The wrong vial dimensions may lead to poor needle alignment, sample loss, or even contamination, which can compromise your chromatographic results.
In manual injection systems, vial dimensions affect how easily a syringe or pipette can access the sample. In automated HPLC systems, precise vial fit ensures accurate injection and prevents needle damage. Additionally, vial neck width determines how well volatile or viscous samples are handled, affecting sample recovery and evaporation rates.
So, how do you choose the best vial diameter and neck size for your analysis? This guide will explore their impact on sample handling, contamination prevention, and HPLC system efficiency, along with practical tips for selecting the right vial for your workflow.
How Vial Dimensions Affect the Sample Injection Process
HPLC vial dimensions—including outer diameter, neck size, and total height—play a critical role in how efficiently and accurately samples are injected. Here’s why these factors matter:
1. Needle Alignment and Sample Accessibility
- If a vial is too wide for the autosampler tray, it may not fit properly, causing misalignment and needle bending during injection.
- If a vial is too narrow, the needle may struggle to reach the sample, leading to inconsistent injections.
- Shallow vials may not provide enough sample depth for the needle to fully submerge, increasing the risk of air bubbles in the injection port.
2. Sample Transfer Efficiency
- In manual injection, a wider vial diameter makes it easier to insert a syringe or pipette without touching the vial walls, reducing contamination risk.
- In automated systems, a consistent vial diameter ensures that the robotic arm accurately picks up the vial, preventing misalignment errors.
3. Risk of Sample Carryover
- Small-diameter vials may cause the autosampler needle to touch the vial walls, leading to carryover contamination between injections.
- Wider vials with proper depth allow needles to fully submerge in the sample without contacting the sides, ensuring a clean sample draw.
Have you ever experienced injection errors due to vial size issues? How did you troubleshoot them?


Choosing the Right Vial Size for Different Injection Systems
Not all vials work for every HPLC setup. The ideal vial depends on whether you use a manual injector or an automated system:
1. Manual Injection: Ease of Handling Matters
- Choose wide-neck vials (wide-mouth vials) to allow easy access with a syringe or pipette.
- Standard 12×32 mm vials with a 9 mm opening are commonly used for manual injection.
- Avoid vials with very narrow necks, as they can make it difficult to retrieve the full sample without touching the vial walls.
2. Automated Injection: Precision and Fit Are Key
- Most autosamplers require 2 mL vials with a 12×32 mm standard size to fit properly in the tray.
- Ensure that the vial height matches your system’s needle depth settings to avoid incomplete sample pickup.
- For high-throughput analysis, consider robotic-compatible vials with consistent dimensions to prevent misalignment.
3. Specialized Applications
- For large-volume samples, use 4 mL vials in specialized autosampler trays.
- For trace analysis or small sample volumes, use low-volume inserts inside a standard 2 mL vial to reduce dead volume and minimize sample waste.
Does your lab use different vial sizes for different injection systems? What challenges have you faced with vial compatibility?
The Role of Narrow vs. Wide Neck Vials in Handling Volatile or Viscous Samples
The neck size of an HPLC vial impacts how easily a sample can be withdrawn and how well it resists evaporation or contamination. Here’s how to choose between narrow-neck and wide-neck vials:
1. Narrow-Neck Vials: Best for Reducing Evaporation
- Advantages:
- Reduce sample evaporation, making them ideal for volatile solvents like acetonitrile or methanol.
- Provide a tighter seal, minimizing exposure to air.
- Best for:
- Trace-level analysis where sample loss must be minimized.
- Long-term storage of volatile compounds.
- Potential Downsides:
- Can be difficult to access with a manual pipette or syringe.
- Not ideal for high-viscosity samples, which may stick to the inner walls.
2. Wide-Neck Vials: Ideal for Viscous and Large-Volume Samples
- Advantages:
- Easier for manual pipetting, making sample retrieval more efficient.
- Suitable for high-viscosity liquids like oils, proteins, or syrups.
- Best for:
- Manual injection workflows requiring frequent sample transfers.
- High-throughput analysis where quick sample access is needed.
- Potential Downsides:
- Higher risk of evaporation and contamination compared to narrow-neck vials.
- May not provide as tight of a seal as narrow-neck vials.
Which type of vial neck do you prefer in your lab? Have you encountered issues with evaporation or sample retrieval?
How Proper Vial Fit Prevents Sample Loss and Contaminatio
Ensuring that the vial fits correctly in your HPLC system is critical to avoid sample loss, contamination, and inconsistent injections.
1. Avoiding Sample Spillage
- Using vials that are too small for the autosampler tray can cause spillage during movement.
- Loose-fitting vials may lead to misalignment, resulting in sample carryover and waste.
2. Preventing Cross-Contamination
- If a vial doesn’t sit flush in the tray, the needle may scrape against the cap or vial walls, picking up contaminants.
- Always check for proper vial alignment to prevent sample carryover in high-throughput applications.
3. Ensuring Consistent Injection Volumes
- Vials that don’t match the autosampler’s pre-set needle depth can cause incomplete sample withdrawal.
- Adjusting the injection depth settings ensures that the autosampler pulls the correct sample volume without introducing air bubbles.
Have you noticed sample loss due to poor vial fit in your system? How do you prevent cross-contamination in your workflow?

Practical Tips for Ensuring Accurate Vial Injection in Your HPLC System
- Use Standardized Vial Sizes
- Stick to autosampler-compatible 12×32 mm vials unless a special application requires a different size.
- Match Vial Neck Size to Sample Type
- Narrow-neck vials for volatile samples.
- Wide-neck vials for viscous or manually injected samples.
- Check Vial Fit in Autosampler Trays
- Ensure vials sit securely and evenly in the tray to prevent misalignment.
- Adjust Needle Depth as Needed
- Modify autosampler settings to match vial dimensions and avoid incomplete sample withdrawal.
- Use Low-Volume Inserts for Small Samples
- If working with limited sample volumes, use low-volume inserts to reduce sample waste.
Conclusion
The diameter and neck size of an HPLC vial directly impact injection accuracy, sample transfer efficiency, and contamination risk. By selecting the appropriate vial dimensions for your specific injection system and sample type, you can optimize workflow efficiency, minimize errors, and improve data reliability.
Mastelf, with over 13 years of experience in chromatography vials since established in 2011, we can help you find the exact vials you need for your applications.


Our expertise ensures that you get reliable and precise products tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you’re in pharmaceuticals, research, or any other industry relying on HPLC, we understand your needs and are here to support you in making the right purchase.
Reach out to Mastelf, and let us assist you in procuring the perfect vials for your work.
FAQ
- Which vial size is best for automated HPLC systems?
- Standard 2 mL (12×32 mm) vials are best for most autosamplers.
- Do wider-neck vials increase evaporation risk?
- Yes, they do. Use narrow-neck vials for volatile solvents.
- Can I use different vial sizes in the same tray?
- It’s not recommended, as it can cause misalignment issues.
- How do I prevent sample loss during injection?
- Ensure vials fit snugly and adjust needle depth settings properly.
- What’s the best vial for small-volume samples?
- Use low-volume inserts inside a standard 2 mL vial.